What is Milvus?
Everything you need to know about Milvus in less than 10 minutes.
What are vector embeddings?
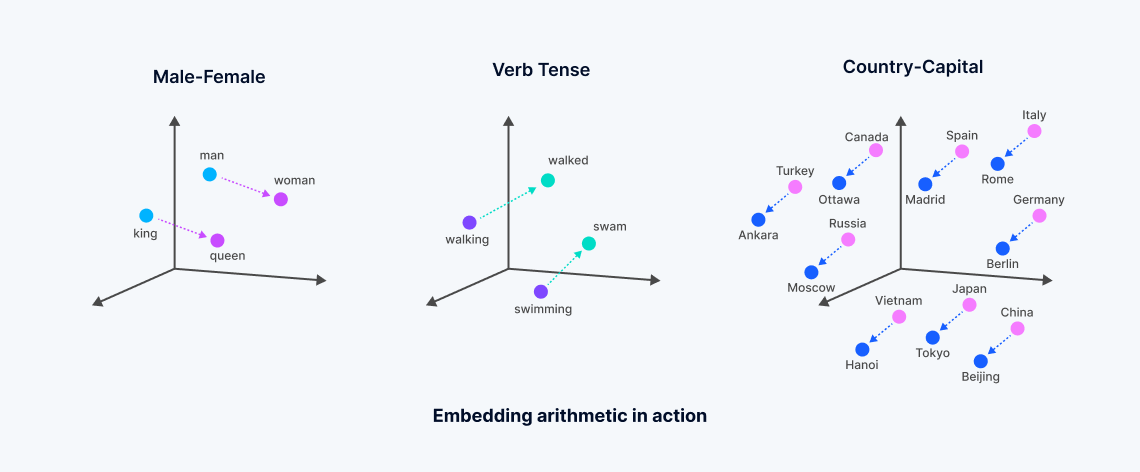
Vector embeddings are numerical representations derived from machine learning models, encapsulating the semantic meaning of unstructured data. These embeddings are generated through the analysis of complex correlations within data by neural networks or transformer architectures, creating a dense vector space where each point corresponds to the "meaning" of data objects, such as words in a document.
This process transforms textual or other unstructured data into vectors that reflect semantic similarities—words with related meanings are positioned closer together in this multi-dimensional space, facilitating a type of search known as "dense vector search." This contrasts with traditional keyword search, which relies on exact matches and uses sparse vectors. The development of vector embeddings, often stemming from foundational models trained extensively by major tech firms, allows for more nuanced searches that capture the essence of the data, moving beyond the limitations of lexical or sparse vector search methods.
What can I use vector embeddings for?
Vector embeddings can be utilized across various applications, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in various ways. Here are some of the most frequent use cases:
Finding Similar Images, Videos, or Audio Files
Vector embeddings enable searching for similar multimedia content by content rather than just keywords, using Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to analyze images, video frames, or audio segments. This allows for advanced searches, like finding images based on sound cues or videos through image queries, by comparing the embedded representations stored in vector databases.
Accelerating Drug Discovery
In the pharmaceutical industry, vector embeddings can encode chemical structures of compounds, facilitating the identification of promising drug candidates by measuring their similarity to target proteins. This accelerates the drug discovery process, saving time and resources by focusing on the most viable leads.
Boosting Search Relevance with Semantic Search
By embedding internal documents into vectors, organizations can leverage semantic search to improve the relevance of search results. This method uses the concept of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to understand the intent behind queries, providing answers from a company's data through AI models like ChatGPT, thereby reducing irrelevant results and AI hallucinations.
Recommender Systems
Vector embeddings revolutionize recommender systems by representing users and items as embeddings to measure similarity. This approach enables personalized recommendations based on individual preferences, enhancing user satisfaction and engagement with online platforms.
Anomaly Detection
In fields such as fraud detection, network security, and industrial monitoring, vector embeddings are instrumental in identifying unusual patterns. Data points represented as embeddings allow for detecting anomalies by calculating distances or dissimilarities, facilitating early identification and preventive measures against potential issues.
What are vector databases?
Vector databases are specialized systems designed for managing and retrieving unstructured data through vector embeddings and numerical representations that capture the essence of data items like images, audio, videos, and textual content. Unlike traditional relational databases that handle structured data with precise search operations, vector databases excel in semantic similarity searches using techniques such as the Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) algorithm. This capability is crucial for developing applications across various domains, including recommender systems, chatbots, and multimedia content search tools, and for addressing the challenges posed by AI and large language models like ChatGPT, such as understanding context and nuances and AI hallucination.
The advent of vector databases like Milvus is transforming industries by enabling content-based searches across a vast array of unstructured data, moving beyond the constraints of human-generated labels. Key features that set vector databases apart include
Scalability and tunability to handle growing data volumes
Multi-tenancy and data isolation for efficient resource use and privacy
A comprehensive suite of APIs for diverse programming languages
User-friendly interfaces that simplify interaction with complex data.
These attributes ensure that vector databases can meet the demands of modern applications, offering powerful tools for exploring and leveraging unstructured data in ways traditional databases cannot.
Vector Database vs. Vector Search Library
Vector search libraries like FAISS, ScaNN, and HNSW offer foundational tools for building prototype systems capable of performing efficient similarity searches and dense vector clustering. These libraries, while powerful and open-source, are designed primarily for vector retrieval and offer rapid setup with capabilities like handling large vector collections and providing interfaces for evaluation and parameter tuning. However, they fall short in terms of scalability, multi-tenancy, and dynamic data modification, making them less suitable for larger, more complex datasets and growing user bases.
In contrast, vector databases emerge as a more comprehensive solution designed to accommodate the storage and real-time retrieval of millions to billions of vectors. They provide a higher level of abstraction, scalability, cloud-nativity, and user-friendly features that surpass the basic functionalities of vector search libraries. While libraries like FAISS are integral components that vector databases may build upon, the latter are full-fledged services that simplify operations like data insertion and management, making them more aligned with the demands of large-scale, dynamic applications in the realm of unstructured data processing.
Vector Databases vs. Vector search plugins for traditional databases
Vector databases and vector search plugins for traditional databases serve distinct roles in handling vector-based searches. Plugins like those in Elasticsearch 8.0 offer vector search capabilities within existing database architectures, functioning as enhancements rather than comprehensive solutions. These plugins lack a full-stack approach to embedding management and vector search, resulting in limitations and suboptimal performance for unstructured data applications.
Key features such as tunability and user-friendly APIs/SDKs, essential for effective vector database operation, are notably absent in vector search plugins. For instance, Elasticsearch's ANN engine, while supporting basic vector storage and querying, is limited by its indexing algorithm and distance metric options, offering less flexibility compared to a dedicated vector database like Milvus. Milvus, designed from the ground up as a vector database, provides a more intuitive API, broader support for indexing methods and distance metrics, and the potential for SQL-like querying, highlighting its superiority in managing and querying unstructured data. This fundamental difference underscores why vector databases, with their comprehensive feature sets and architecture tailored for unstructured data, are preferred over vector search plugins for achieving optimal search and management of vector embeddings.
How does Milvus differentiate from other vector databases?
Milvus stands out as a vector database with its scalable architecture and diverse capabilities designed to accelerate and unify search experiences across various applications. The key feature highlights are:
Scalable and Elastic Architecture
Milvus is engineered for exceptional scalability and elasticity, accommodating the dynamic demands of modern applications. It achieves this through service-oriented design, decoupling storage, coordinators, and workers, allowing for component-wise scaling. This modular approach ensures that different computational tasks can scale independently according to varying workloads, providing fine-grained resource allocation and isolation.
Diverse Index Support
Milvus supports an extensive array of over 10 index types, including widely-used ones such as HNSW, IVF, Product Quantization, and GPU-based indexing. This variety empowers developers to optimize searches according to specific performance and accuracy requirements, ensuring that the database can adapt to a wide range of applications and data characteristics. Continuous expansion of its index offerings, e.g. GPU index, further enhances Milvus's adaptability and effectiveness in handling complex search tasks.
Versatile Search Capabilities
Milvus offers a wide range of search types, including top-K Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN), Range ANN, and search with metadata filtering, and upcoming hybrid dense and sparse vector search. This diversity enables unmatched query flexibility and precision, granting developers the ability to customize data retrieval strategies to meet specific application demands, thereby optimizing both the relevance and efficiency of search results.
Tunable Consistency
Milvus offers a delta consistency model that allows users to specify a "staleness tolerance" for query data, enabling a tailored balance between query performance and data freshness. This flexibility is crucial for applications requiring up-to-date results without sacrificing response times, effectively supporting both strong and eventual consistency as per application needs.
Hardware-Accelerated Compute Support
Milvus is designed to leverage various types of compute capabilities, such as AVX512 and Neon for SIMD execution, alongside quantization, cache-aware optimizations, and GPU support. This approach enables efficient utilization of specific hardware strengths, ensuring rapid processing and cost-effective scalability. By tailoring resource use to the unique demands of different applications, Milvus enhances both the speed and efficiency of vector data management and search operations.
How does Milvus work in a nutshell?
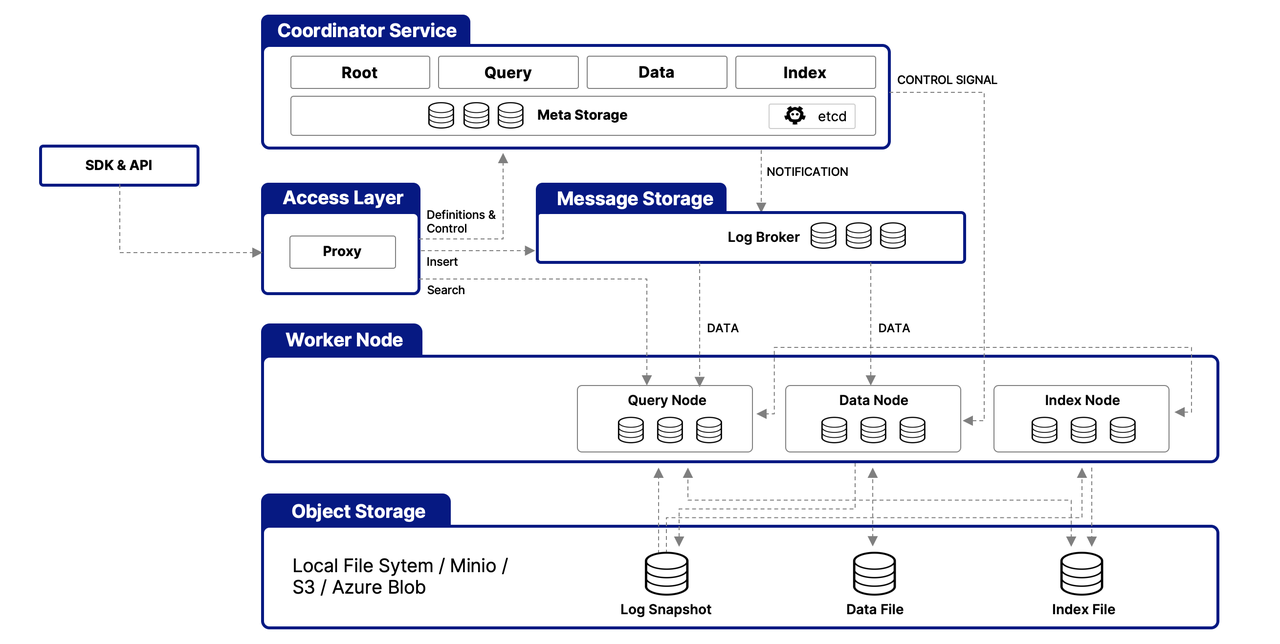
Milvus is structured around a multi-layered architecture designed to efficiently handle and process vector data, ensuring scalability, tunability, and data isolation. Here's a simplified overview of its architecture:
Access Layer
This layer serves as the initial point of contact for external requests, utilizing stateless proxies for client connection management, static verification, and dynamic checks. These proxies also handle load balancing and are key to implementing Milvus's comprehensive API suite. Once the downstream service processes a request, the access layer routes the response back to the user.
Coordinator Service
Acting as the central command, this service orchestrates load balancing and data management through four coordinators, which ensure efficient data, query, and index management.
The Root Coordinator: managing data-related tasks and global timestamps
The Query Coordinator: overseeing query nodes for search operations
The Data Coordinator: handling data nodes and metadata
The Index Coordinator: maintaining index nodes and metadata
Worker Nodes
Responsible for the actual execution of tasks, worker nodes are scalable pods that carry out commands from coordinators. They enable Milvus to adjust dynamically to changing data, query, and indexing demands, supporting the system's scalability and tunability.
Object Storage Layer
Fundamental for data persistence, this layer consists of
Meta store: using etcd for metadata snapshots and system health checks
Log broker: for streaming data persistence and recovery, utilizing Pulsar or RocksDB
Object storage: storing log snapshots, index files, and query results, with support for services like AWS S3, Azure Blob Storage, and MinIO
Where to go from here?
- To get hands-on experience with Milvus, follow the get started guide.
- To understand Milvus in more detail, read the Documentation.
- Browse through the Use Cases to learn how other users in our worldwide community are getting value from Milvus.
Join a local Unstructured Data meetup and our Discord.