Contextual Retrieval with Milvus
 image
Contextual Retrieval is an advanced retrieval method proposed by Anthropic to address the issue of semantic isolation of chunks, which arises in current Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) solutions. In the current practical RAG paradigm, documents are divided into several chunks, and a vector database is used to search for the query, retrieving the most relevant chunks. An LLM then responds to the query using these retrieved chunks. However, this chunking process can result in the loss of contextual information, making it difficult for the retriever to determine relevance.
image
Contextual Retrieval is an advanced retrieval method proposed by Anthropic to address the issue of semantic isolation of chunks, which arises in current Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) solutions. In the current practical RAG paradigm, documents are divided into several chunks, and a vector database is used to search for the query, retrieving the most relevant chunks. An LLM then responds to the query using these retrieved chunks. However, this chunking process can result in the loss of contextual information, making it difficult for the retriever to determine relevance.
Contextual Retrieval improves traditional retrieval systems by adding relevant context to each document chunk before embedding or indexing, boosting accuracy and reducing retrieval errors. Combined with techniques like hybrid retrieval and reranking, it enhances Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems, especially for large knowledge bases. Additionally, it offers a cost-effective solution when paired with prompt caching, significantly reducing latency and operational costs, with contextualized chunks costing approximately $1.02 per million document tokens. This makes it a scalable and efficient approach for handling large knowledge bases. Anthropic’s solution shows two insightful aspects:
Document Enhancement: Query rewriting is a crucial technique in modern information retrieval, often using auxiliary information to make the query more informative. Similarly, to achieve better performance in RAG, preprocessing documents with an LLM (e.g., cleaning the data source, complementing lost information, summarizing, etc.) before indexing can significantly improve the chances of retrieving relevant documents. In other words, this preprocessing step helps bring the documents closer to the queries in terms of relevance.Low-Cost Processing by Caching Long Context: One common concern when using LLMs to process documents is the cost. The KVCache is a popular solution that allows reuse of intermediate results for the same preceding context. While most hosted LLM vendors make this feature transparent to user, Anthropic gives users control over the caching process. When a cache hit occurs, most computations can be saved (this is common when the long context remains the same, but the instruction for each query changes). For more details, click here.
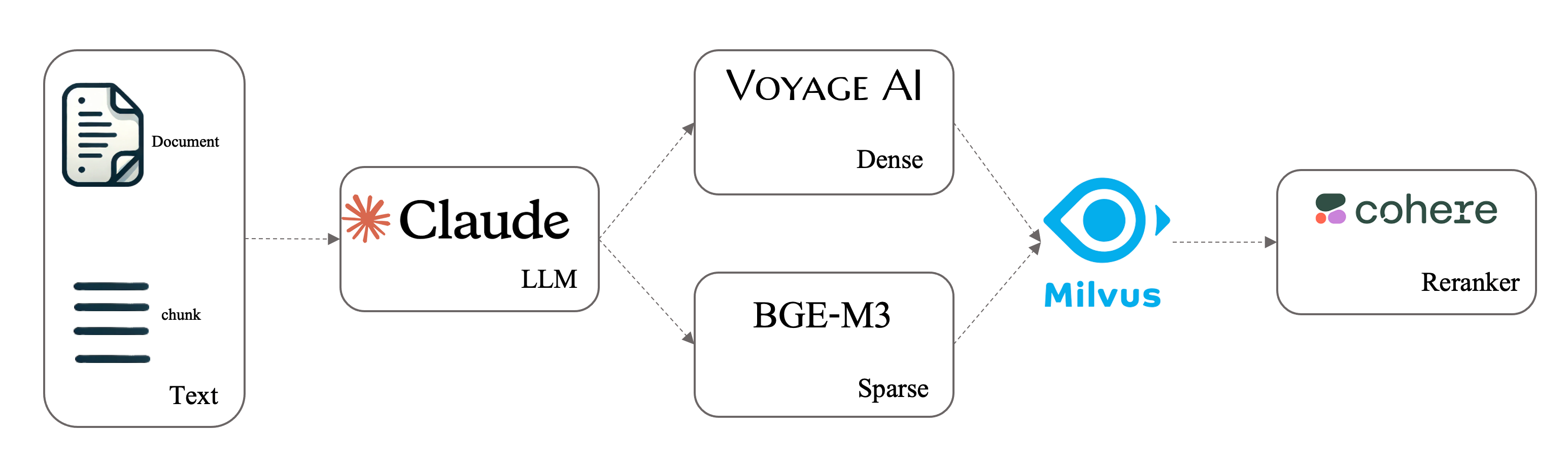
In this notebook, we will demonstrate how to perform contextual retrieval using Milvus with an LLM, combining dense-sparse hybrid retrieval and a reranker to create a progressively more powerful retrieval system. The data and experimental setup are based on the contextual retrieval.
Preparation
Install Dependencies
$ pip install "pymilvus[model]"
$ pip install tqdm
$ pip install anthropic
If you are using Google Colab, to enable dependencies just installed, you may need to restart the runtime (click on the “Runtime” menu at the top of the screen, and select “Restart session” from the dropdown menu).
You will need API keys from Cohere, Voyage, and Anthropic to run the code.
Download Data
The following command will download the example data used in original Anthropic demo.
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/anthropics/anthropic-cookbook/refs/heads/main/skills/contextual-embeddings/data/codebase_chunks.json
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/anthropics/anthropic-cookbook/refs/heads/main/skills/contextual-embeddings/data/evaluation_set.jsonl
Define Retriever
This class is designed to be flexible, allowing you to choose between different retrieval modes based on your needs. By specifying options in the initialization method, you can determine whether to use contextual retrieval, hybrid search (combining dense and sparse retrieval methods), or a reranker for enhanced results.
from pymilvus.model.dense import VoyageEmbeddingFunction
from pymilvus.model.hybrid import BGEM3EmbeddingFunction
from pymilvus.model.reranker import CohereRerankFunction
from typing import List, Dict, Any
from typing import Callable
from pymilvus import (
MilvusClient,
DataType,
AnnSearchRequest,
RRFRanker,
)
from tqdm import tqdm
import json
import anthropic
class MilvusContextualRetriever:
def __init__(
self,
uri="milvus.db",
collection_name="contexual_bgem3",
dense_embedding_function=None,
use_sparse=False,
sparse_embedding_function=None,
use_contextualize_embedding=False,
anthropic_client=None,
use_reranker=False,
rerank_function=None,
):
self.collection_name = collection_name
# For Milvus-lite, uri is a local path like "./milvus.db"
# For Milvus standalone service, uri is like "http://localhost:19530"
# For Zilliz Clond, please set `uri` and `token`, which correspond to the [Public Endpoint and API key](https://docs.zilliz.com/docs/on-zilliz-cloud-console#cluster-details) in Zilliz Cloud.
self.client = MilvusClient(uri)
self.embedding_function = dense_embedding_function
self.use_sparse = use_sparse
self.sparse_embedding_function = None
self.use_contextualize_embedding = use_contextualize_embedding
self.anthropic_client = anthropic_client
self.use_reranker = use_reranker
self.rerank_function = rerank_function
if use_sparse is True and sparse_embedding_function:
self.sparse_embedding_function = sparse_embedding_function
elif sparse_embedding_function is False:
raise ValueError(
"Sparse embedding function cannot be None if use_sparse is False"
)
else:
pass
def build_collection(self):
schema = self.client.create_schema(
auto_id=True,
enable_dynamic_field=True,
)
schema.add_field(field_name="pk", datatype=DataType.INT64, is_primary=True)
schema.add_field(
field_name="dense_vector",
datatype=DataType.FLOAT_VECTOR,
dim=self.embedding_function.dim,
)
if self.use_sparse is True:
schema.add_field(
field_name="sparse_vector", datatype=DataType.SPARSE_FLOAT_VECTOR
)
index_params = self.client.prepare_index_params()
index_params.add_index(
field_name="dense_vector", index_type="FLAT", metric_type="IP"
)
if self.use_sparse is True:
index_params.add_index(
field_name="sparse_vector",
index_type="SPARSE_INVERTED_INDEX",
metric_type="IP",
)
self.client.create_collection(
collection_name=self.collection_name,
schema=schema,
index_params=index_params,
enable_dynamic_field=True,
)
def insert_data(self, chunk, metadata):
dense_vec = self.embedding_function([chunk])[0]
if self.use_sparse is True:
sparse_result = self.sparse_embedding_function.encode_documents([chunk])
if type(sparse_result) == dict:
sparse_vec = sparse_result["sparse"][[0]]
else:
sparse_vec = sparse_result[[0]]
self.client.insert(
collection_name=self.collection_name,
data={
"dense_vector": dense_vec,
"sparse_vector": sparse_vec,
**metadata,
},
)
else:
self.client.insert(
collection_name=self.collection_name,
data={"dense_vector": dense_vec, **metadata},
)
def insert_contextualized_data(self, doc, chunk, metadata):
contextualized_text, usage = self.situate_context(doc, chunk)
metadata["context"] = contextualized_text
text_to_embed = f"{chunk}\n\n{contextualized_text}"
dense_vec = self.embedding_function([text_to_embed])[0]
if self.use_sparse is True:
sparse_vec = self.sparse_embedding_function.encode_documents(
[text_to_embed]
)["sparse"][[0]]
self.client.insert(
collection_name=self.collection_name,
data={
"dense_vector": dense_vec,
"sparse_vector": sparse_vec,
**metadata,
},
)
else:
self.client.insert(
collection_name=self.collection_name,
data={"dense_vector": dense_vec, **metadata},
)
def situate_context(self, doc: str, chunk: str):
DOCUMENT_CONTEXT_PROMPT = """
<document>
{doc_content}
</document>
"""
CHUNK_CONTEXT_PROMPT = """
Here is the chunk we want to situate within the whole document
<chunk>
{chunk_content}
</chunk>
Please give a short succinct context to situate this chunk within the overall document for the purposes of improving search retrieval of the chunk.
Answer only with the succinct context and nothing else.
"""
response = self.anthropic_client.beta.prompt_caching.messages.create(
model="claude-3-haiku-20240307",
max_tokens=1000,
temperature=0.0,
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "text",
"text": DOCUMENT_CONTEXT_PROMPT.format(doc_content=doc),
"cache_control": {
"type": "ephemeral"
}, # we will make use of prompt caching for the full documents
},
{
"type": "text",
"text": CHUNK_CONTEXT_PROMPT.format(chunk_content=chunk),
},
],
},
],
extra_headers={"anthropic-beta": "prompt-caching-2024-07-31"},
)
return response.content[0].text, response.usage
def search(self, query: str, k: int = 20) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
dense_vec = self.embedding_function([query])[0]
if self.use_sparse is True:
sparse_vec = self.sparse_embedding_function.encode_queries([query])[
"sparse"
][[0]]
req_list = []
if self.use_reranker:
k = k * 10
if self.use_sparse is True:
req_list = []
dense_search_param = {
"data": [dense_vec],
"anns_field": "dense_vector",
"param": {"metric_type": "IP"},
"limit": k * 2,
}
dense_req = AnnSearchRequest(**dense_search_param)
req_list.append(dense_req)
sparse_search_param = {
"data": [sparse_vec],
"anns_field": "sparse_vector",
"param": {"metric_type": "IP"},
"limit": k * 2,
}
sparse_req = AnnSearchRequest(**sparse_search_param)
req_list.append(sparse_req)
docs = self.client.hybrid_search(
self.collection_name,
req_list,
RRFRanker(),
k,
output_fields=[
"content",
"original_uuid",
"doc_id",
"chunk_id",
"original_index",
"context",
],
)
else:
docs = self.client.search(
self.collection_name,
data=[dense_vec],
anns_field="dense_vector",
limit=k,
output_fields=[
"content",
"original_uuid",
"doc_id",
"chunk_id",
"original_index",
"context",
],
)
if self.use_reranker and self.use_contextualize_embedding:
reranked_texts = []
reranked_docs = []
for i in range(k):
if self.use_contextualize_embedding:
reranked_texts.append(
f"{docs[0][i]['entity']['content']}\n\n{docs[0][i]['entity']['context']}"
)
else:
reranked_texts.append(f"{docs[0][i]['entity']['content']}")
results = self.rerank_function(query, reranked_texts)
for result in results:
reranked_docs.append(docs[0][result.index])
docs[0] = reranked_docs
return docs
def evaluate_retrieval(
queries: List[Dict[str, Any]], retrieval_function: Callable, db, k: int = 20
) -> Dict[str, float]:
total_score = 0
total_queries = len(queries)
for query_item in tqdm(queries, desc="Evaluating retrieval"):
query = query_item["query"]
golden_chunk_uuids = query_item["golden_chunk_uuids"]
# Find all golden chunk contents
golden_contents = []
for doc_uuid, chunk_index in golden_chunk_uuids:
golden_doc = next(
(
doc
for doc in query_item["golden_documents"]
if doc["uuid"] == doc_uuid
),
None,
)
if not golden_doc:
print(f"Warning: Golden document not found for UUID {doc_uuid}")
continue
golden_chunk = next(
(
chunk
for chunk in golden_doc["chunks"]
if chunk["index"] == chunk_index
),
None,
)
if not golden_chunk:
print(
f"Warning: Golden chunk not found for index {chunk_index} in document {doc_uuid}"
)
continue
golden_contents.append(golden_chunk["content"].strip())
if not golden_contents:
print(f"Warning: No golden contents found for query: {query}")
continue
retrieved_docs = retrieval_function(query, db, k=k)
# Count how many golden chunks are in the top k retrieved documents
chunks_found = 0
for golden_content in golden_contents:
for doc in retrieved_docs[0][:k]:
retrieved_content = doc["entity"]["content"].strip()
if retrieved_content == golden_content:
chunks_found += 1
break
query_score = chunks_found / len(golden_contents)
total_score += query_score
average_score = total_score / total_queries
pass_at_n = average_score * 100
return {
"pass_at_n": pass_at_n,
"average_score": average_score,
"total_queries": total_queries,
}
def retrieve_base(query: str, db, k: int = 20) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
return db.search(query, k=k)
def load_jsonl(file_path: str) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""Load JSONL file and return a list of dictionaries."""
with open(file_path, "r") as file:
return [json.loads(line) for line in file]
def evaluate_db(db, original_jsonl_path: str, k):
# Load the original JSONL data for queries and ground truth
original_data = load_jsonl(original_jsonl_path)
# Evaluate retrieval
results = evaluate_retrieval(original_data, retrieve_base, db, k)
print(f"Pass@{k}: {results['pass_at_n']:.2f}%")
print(f"Total Score: {results['average_score']}")
print(f"Total queries: {results['total_queries']}")
Now you need to initialize these models for the following experiments. You can easily switch to other models using the PyMilvus model library.
dense_ef = VoyageEmbeddingFunction(api_key="your-voyage-api-key", model_name="voyage-2")
sparse_ef = BGEM3EmbeddingFunction()
cohere_rf = CohereRerankFunction(api_key="your-cohere-api-key")
Fetching 30 files: 0%| | 0/30 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
path = "codebase_chunks.json"
with open(path, "r") as f:
dataset = json.load(f)
Experiment I: Standard Retrieval
Standard retrieval uses only dense embeddings to retrieve related documents. In this experiment, we will use Pass@5 to reproduce the results from the original repo.
standard_retriever = MilvusContextualRetriever(
uri="standard.db", collection_name="standard", dense_embedding_function=dense_ef
)
standard_retriever.build_collection()
for doc in dataset:
doc_content = doc["content"]
for chunk in doc["chunks"]:
metadata = {
"doc_id": doc["doc_id"],
"original_uuid": doc["original_uuid"],
"chunk_id": chunk["chunk_id"],
"original_index": chunk["original_index"],
"content": chunk["content"],
}
chunk_content = chunk["content"]
standard_retriever.insert_data(chunk_content, metadata)
evaluate_db(standard_retriever, "evaluation_set.jsonl", 5)
Evaluating retrieval: 100%|██████████| 248/248 [01:29<00:00, 2.77it/s]
Pass@5: 80.92%
Total Score: 0.8091877880184332
Total queries: 248
Experiment II: Hybrid Retrieval
Now that we’ve obtained promising results with the Voyage embedding, we will move on to performing hybrid retrieval using the BGE-M3 model which generates powerful sparse embeddings. The results from dense retrieval and sparse retrieval will be combined using the Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF) method to produce a hybrid result.
hybrid_retriever = MilvusContextualRetriever(
uri="hybrid.db",
collection_name="hybrid",
dense_embedding_function=dense_ef,
use_sparse=True,
sparse_embedding_function=sparse_ef,
)
hybrid_retriever.build_collection()
for doc in dataset:
doc_content = doc["content"]
for chunk in doc["chunks"]:
metadata = {
"doc_id": doc["doc_id"],
"original_uuid": doc["original_uuid"],
"chunk_id": chunk["chunk_id"],
"original_index": chunk["original_index"],
"content": chunk["content"],
}
chunk_content = chunk["content"]
hybrid_retriever.insert_data(chunk_content, metadata)
evaluate_db(hybrid_retriever, "evaluation_set.jsonl", 5)
Evaluating retrieval: 100%|██████████| 248/248 [02:09<00:00, 1.92it/s]
Pass@5: 84.69%
Total Score: 0.8469182027649771
Total queries: 248
Experiment III: Contextual Retrieval
Hybrid retrieval shows an improvement, but the results can be further enhanced by applying a contextual retrieval method. To achieve this, we will use Anthropic’s language model to prepend the context from whole document for each chunk.
anthropic_client = anthropic.Anthropic(
api_key="your-anthropic-api-key",
)
contextual_retriever = MilvusContextualRetriever(
uri="contextual.db",
collection_name="contextual",
dense_embedding_function=dense_ef,
use_sparse=True,
sparse_embedding_function=sparse_ef,
use_contextualize_embedding=True,
anthropic_client=anthropic_client,
)
contextual_retriever.build_collection()
for doc in dataset:
doc_content = doc["content"]
for chunk in doc["chunks"]:
metadata = {
"doc_id": doc["doc_id"],
"original_uuid": doc["original_uuid"],
"chunk_id": chunk["chunk_id"],
"original_index": chunk["original_index"],
"content": chunk["content"],
}
chunk_content = chunk["content"]
contextual_retriever.insert_contextualized_data(
doc_content, chunk_content, metadata
)
evaluate_db(contextual_retriever, "evaluation_set.jsonl", 5)
Evaluating retrieval: 100%|██████████| 248/248 [01:55<00:00, 2.15it/s]
Pass@5: 87.14%
Total Score: 0.8713517665130568
Total queries: 248
Experiment IV: Contextual Retrieval with Reranker
The results can be further improved by adding a Cohere reranker. Without initializing a new retriever with reranker separately, we can simply configure the existing retriever to use the reranker for enhanced performance.
contextual_retriever.use_reranker = True
contextual_retriever.rerank_function = cohere_rf
evaluate_db(contextual_retriever, "evaluation_set.jsonl", 5)
Evaluating retrieval: 100%|██████████| 248/248 [02:02<00:00, 2.00it/s]
Pass@5: 90.91%
Total Score: 0.9090821812596005
Total queries: 248
We have demonstrated several methods to improve retrieval performance. With more ad-hoc design tailored to the scenario, contextual retrieval shows significant potential to preprocess documents at a low cost, leading to a better RAG system.
