RBAC Explained
RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) is an access control method based on roles. With RBAC, you can finely control the operations users can perform at the collection, database, and instance levels, enhancing data security.
Unlike traditional user access control models, RBAC introduces the concept of roles. In the RBAC model, you grant privileges to roles and then grant those roles to users. Then users can obtain privileges.
The RBAC model can improve the efficiency of access control management. For example, if multiple users require the same set of privileges, you do not need to manually set the privileges for each user. Instead, you can create a role and assign the role to users. If you want to adjust the privileges of these users, you can just adjust the role privileges and the modification will be applied to all users with this role.
RBAC key concepts
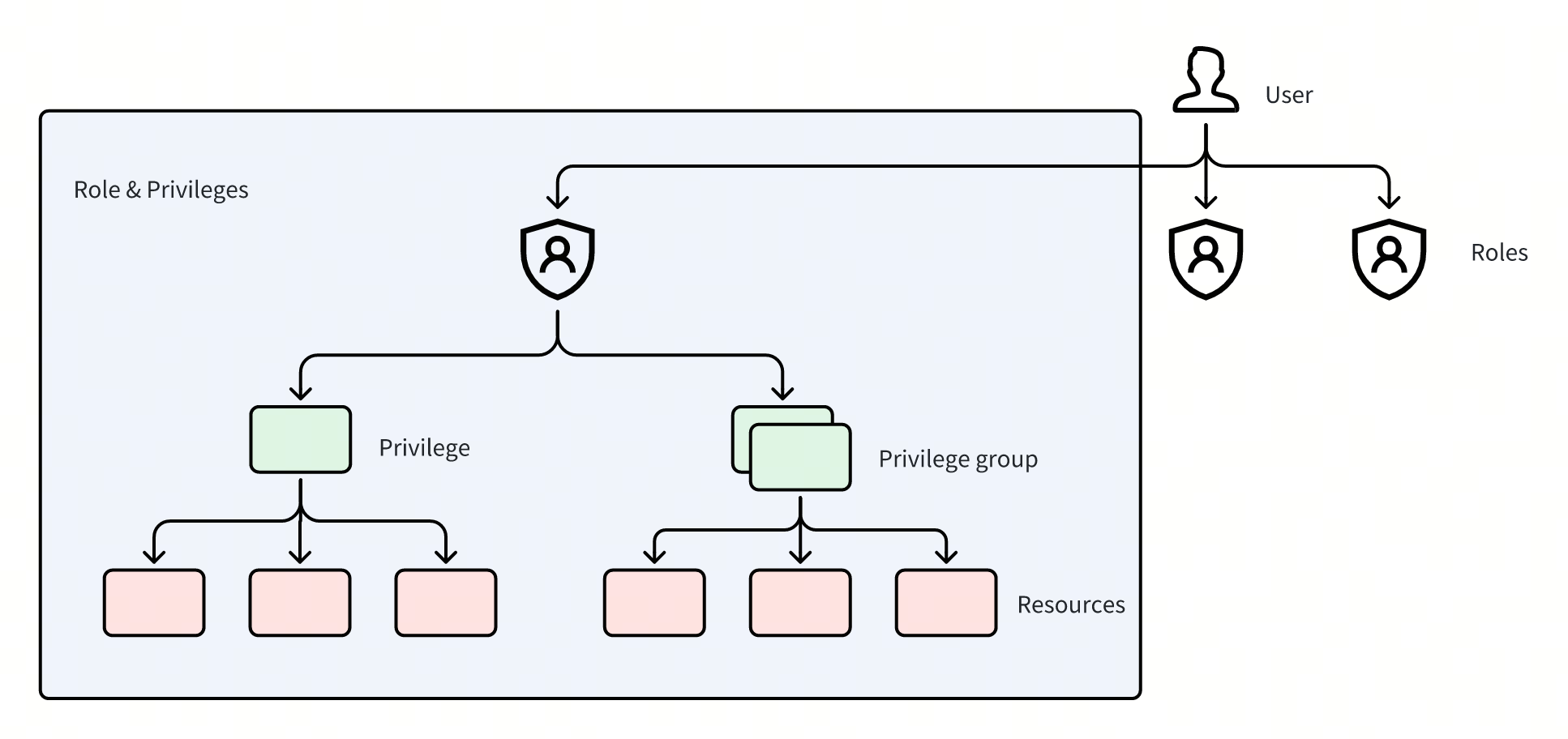 Users, roles, and privileges
Users, roles, and privileges
There are four major components in the RBAC model.
**Resource: **The resource entity that can be accessed. There are three levels of resources in Milvus - instance, database, and collection.
**Privilege: **The permission to perform certain operations on Milvus resources (eg. create collections, insert data, etc).
**Privilege group: **A group of multiple privileges.
**Role: **A role consists of two parts-privileges and resources. Privileges define the type of operations that a role can perform while resources define the target resources that the operations can be performed on. For example, the database administrator role can perform read, write, and manage operations on certain databases.
**User: **A user is someone who uses Milvus. Each user has a unique ID and is granted a role or multiple roles.
Procedures
The achieve access control via RBAC, you need to follow the steps below:
Create a user: In addition to the default user
rootin Milvus, you can create new users and set passwords to protect data security.Create a role: You can create customized roles based on your needs. The specific capabilities of a role are determined by its privileges.
Create a privilege group: Combine multiple privileges into one privilege group to streamline the process of granting privileges to a role.
Grant privileges or privilege groups to a role: Define the capabilities of a role be granting privileges or privilege groups to this role.
Grant roles to users: Grant roles with certain privileges to users so that users can have the privileges of a role. A single role can be granted to multiple users.