GPU Index
Milvus supports various GPU index types to accelerate search performance and efficiency, especially in high-throughput, and high-recall scenarios. This topic provides an overview of the GPU index types supported by Milvus, their suitable use cases, and performance characteristics. For information on building indexes with GPU, refer to Index with GPU.
It’s important to note that using a GPU index may not necessarily reduce latency compared to using a CPU index. If you want to fully maximize throughput, you will need extremely high request pressure or a large number of query vectors.
 performance
performance
Milvus’ GPU support is contributed by Nvidia RAPIDS team. The following are the GPU index types currently supported by Milvus.
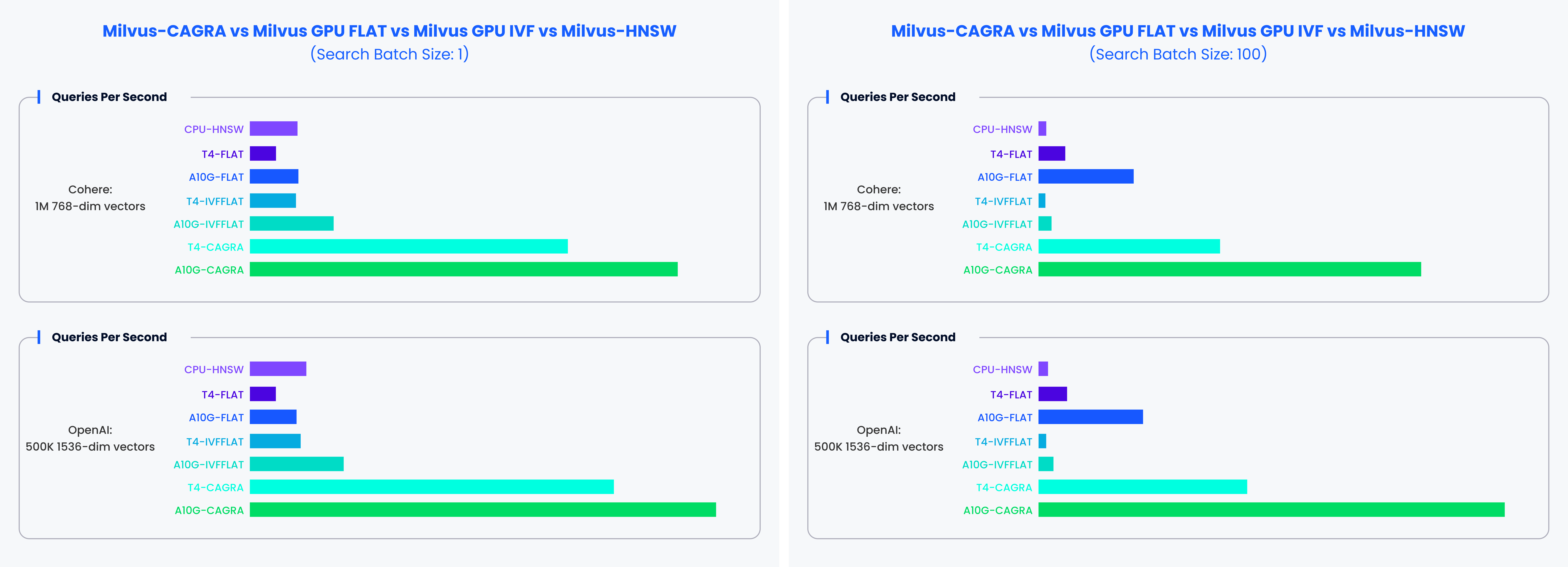
GPU_CAGRA
GPU_CAGRA is a graph-based index optimized for GPUs, Using inference-grade GPUs to run the Milvus GPU version can be more cost-effective compared to using expensive training-grade GPUs.
Index building parameters
Parameter Description Default Value intermediate_graph_degreeAffects recall and build time by determining the graph’s degree before pruning. Recommended values are 32or64.128graph_degreeAffects search performance and recall by setting the graph’s degree after pruning. A larger difference between these two degrees results in a longer build time. Its value must be smaller than the value of intermediate_graph_degree. 64build_algoSelects the graph generation algorithm before pruning. Possible values: IVF_PQ: Offers higher quality but slower build time.NN_DESCENT: Provides a quicker build with potentially lower recall.IVF_PQcache_dataset_on_deviceDecides whether to cache the original dataset in GPU memory. Possible values: “true”: Caches the original dataset to enhance recall by refining search results.“false”: Does not cache the original dataset to save gpu memory.“false”adapt_for_cpuDecides whether to use GPU for index-building and CPU for search.
Setting this parameter totruerequires the presence of theefparameter in the search requests.“false”Search parameters
Parameter Description Default Value itopk_sizeDetermines the size of intermediate results kept during the search. A larger value may improve recall at the expense of search performance. It should be at least equal to the final top-k (limit) value and is typically a power of 2 (e.g., 16, 32, 64, 128). Empty search_widthSpecifies the number of entry points into the CAGRA graph during the search. Increasing this value can enhance recall but may impact search performance(e.g. 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32). Empty min_iterations/max_iterationsControls the search iteration process. By default, they are set to 0, and CAGRA automatically determines the number of iterations based onitopk_sizeandsearch_width. Adjusting these values manually can help balance performance and accuracy.0team_sizeSpecifies the number of CUDA threads used for calculating metric distance on the GPU. Common values are a power of 2 up to 32 (e.g. 2, 4, 8, 16, 32). It has a minor impact on search performance. The default value is 0, where Milvus automatically selects theteam_sizebased on the vector dimension.0efSpecifies the query time/accuracy trade-off. A higher efvalue leads to more accurate but slower search.
This parameter is mandatory if you setadapt_for_cputotruewhen you build the index.[top_k, int_max]
Limits on search
Parameter Range limit(top-K)<= 1024 limit(top-K)<=max(( itopk_size+ 31)// 32,search_width) * 32
GPU_IVF_FLAT
Similar to IVF_FLAT, GPU_IVF_FLAT also divides vector data into nlist cluster units, and then compares distances between the target input vector and the center of each cluster. Depending on the number of clusters the system is set to query (nprobe), similarity search results are returned based on comparisons between the target input and the vectors in the most similar cluster(s) only — drastically reducing query time.
By adjusting nprobe, an ideal balance between accuracy and speed can be found for a given scenario. Results from the IVF_FLAT performance test demonstrate that query time increases sharply as both the number of target input vectors (nq), and the number of clusters to search (nprobe), increase.
GPU_IVF_FLAT is the most basic IVF index, and the encoded data stored in each unit is consistent with the original data.
When conducting searches, note that you can set the top-K up to 256 for any search against a GPU_IVF_FLAT-indexed collection.
Index building parameters
Parameter Description Range Default Value nlistNumber of cluster units [1, 65536] 128cache_dataset_on_deviceDecides whether to cache the original dataset in GPU memory. Possible values: “true”: Caches the original dataset to enhance recall by refining search results.“false”: Does not cache the original dataset to save gpu memory."true""flase""false"Search parameters
Common search
Parameter Description Range Default Value nprobeNumber of units to query [1, nlist] 8
Limits on search
Parameter Range limit(top-K)<= 2048
GPU_IVF_PQ
PQ (Product Quantization) uniformly decomposes the original high-dimensional vector space into Cartesian products of m low-dimensional vector spaces, and then quantizes the decomposed low-dimensional vector spaces. Instead of calculating the distances between the target vector and the center of all the units, product quantization enables the calculation of distances between the target vector and the clustering center of each low-dimensional space and greatly reduces the time complexity and space complexity of the algorithm.
IVF_PQ performs IVF index clustering before quantizing the product of vectors. Its index file is even smaller than IVF_SQ8, but it also causes a loss of accuracy during searching vectors.
Index building parameters and search parameters vary with Milvus distribution. Select your Milvus distribution first.
When conducting searches, note that you can set the top-K up to 8192 for any search against a GPU_IVF_FLAT-indexed collection.
Index building parameters
Parameter Description Range Default Value nlistNumber of cluster units [1, 65536] 128mNumber of factors of product quantization, dim mod m or = 00nbits[Optional] Number of bits in which each low-dimensional vector is stored. [1, 16] 8cache_dataset_on_deviceDecides whether to cache the original dataset in GPU memory. Possible values: “true”: Caches the original dataset to enhance recall by refining search results.“false”: Does not cache the original dataset to save gpu memory."true""false""false"Search parameters
Common search
Parameter Description Range Default Value nprobeNumber of units to query [1, nlist] 8
Limits on search
Parameter Range limit(top-K)<= 1024
GPU_BRUTE_FORCE
GPU_BRUTE_FORCE is tailored for cases where extremely high recall is crucial, guaranteeing a recall of 1 by comparing each query with all vectors in the dataset. It only requires the metric type (metric_type) and top-k (limit) as index building and search parameters.
For GPU_BRUTE_FORCE, no addition index building parameters or search parameters are required.
Conclusion
Currently, Milvus loads all indexes into GPU memory for efficient search operations. The amount of data that can be loaded depends on the size of the GPU memory:
- GPU_CAGRA: Memory usage is approximately 1.8 times that of the original vector data.
- GPU_IVF_FLAT and GPU_BRUTE_FORCE: Requires memory equal to the size of the original data.
- GPU_IVF_PQ: Utilizes a smaller memory footprint, which depends on the compression parameter settings.